Initiatives for Effective Use of Resources Back Number (2019)
Back to Latest Initiatives for Effective Use of Resources
Basic Approach
The MinebeaMitsumi Group recognizes that there are limits to the availability of resources used in its products, which include metals, plastics, and other raw materials, along with oil, natural gas, and other energy sources. Additionally, with regard to rare earth elements indispensable to the manufacture of electronics, since the number of countries producing and exporting the materials is limited, they are more susceptible to export restrictions.
We believe that the effective use of resources is critical to the continuation of our business activities, and to that end we are taking various measures.
Results of FY2018 Initiatives
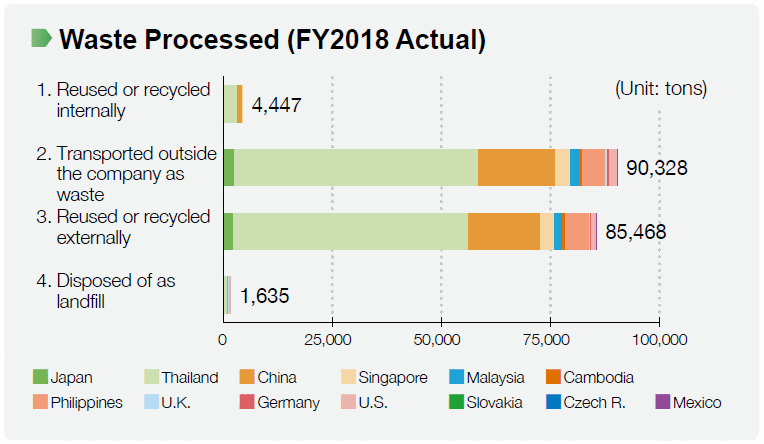 In FY2018, principal raw materials used by the MinebeaMitsumi Group included approximately 102,966 tons of steel and 17,850 tons of resin, and the total amount of materials used increased about 2% compared with FY2017.
In FY2018, principal raw materials used by the MinebeaMitsumi Group included approximately 102,966 tons of steel and 17,850 tons of resin, and the total amount of materials used increased about 2% compared with FY2017.
The amount of landfill waste generated by the Group's operations in FY2018 totaled 1,635 tons, increasing 56 tons compared to FY2017.
At our mass production plants in Thailand and China, we are recycling water inside the plants to the greatest extent possible and prevent external emissions through our "Plant Wastewater Zero System."
Water emissions from Group plants in FY2018 totaled 3,548,735 m3, an increase of 59,391 m3 compared with FY2017.
Responding to CDP Water Security Questionnaire 2018
 The MinebeaMitsumi Group actively undertakes the saving and conservation of water resources, and at the same time, also recognizes the importance of disclosing information about such activities, and therefore responded to the CDP Water Security Questionnaire 2018 conducted by CDP.
The MinebeaMitsumi Group actively undertakes the saving and conservation of water resources, and at the same time, also recognizes the importance of disclosing information about such activities, and therefore responded to the CDP Water Security Questionnaire 2018 conducted by CDP.
Plant Initiatives
Initiatives for Effective Use of Resources (Japan, Thailand, Malaysia, China, and other countries)
The MinebeaMitsumi Group actively takes measures to increase yields in manufacturing and reduce the occurrence of defective products, but when producing electrical and electronic products, generation of leftover electric wire and steel materials, and the occurrence of reject products during manufacturing processes cannot be avoided.
We outsource this type of electrical and electronic waste to processing companies with advanced recycling technologies to break down and sort the waste to the raw material level to the extent possible and recycle it as resources.
Electric wire, for example, comprises copper wire covered by plastic, and resource recycling is not possible with the copper and plastic together. Consequently, discarded electrical wire is finely shredded to a degree that the copper and plastic are separated and the materials are sorted for resource recycling.
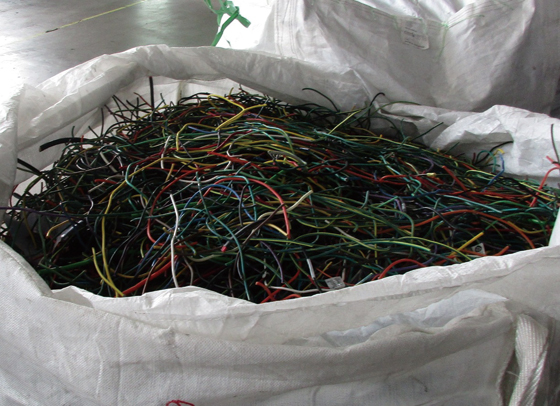

Shredded electric wire
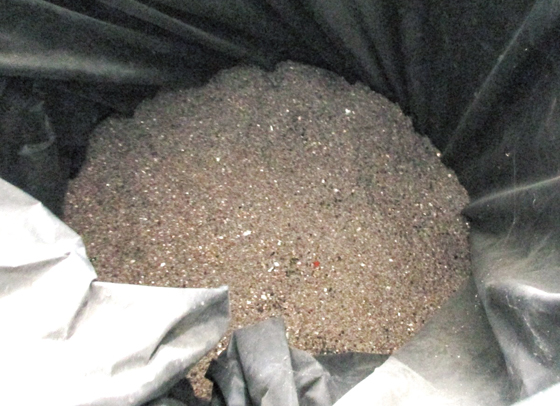

Copper pieces recovered from electric wire
Reuse of Waste Materials Generated at Reconstructed Plants (Japan: Akita Business Division)
When reconstructing a building, the Akita Business Division finely ground up the concrete used in the foundations of the old building and reused it as gravel at the site. The new building (a three-story structure) is scheduled for completion in February 2020.
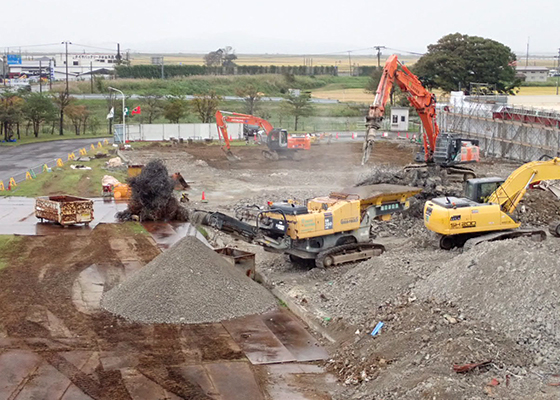

Concrete is ground up by a Galapagos crusher (September–October 2018)
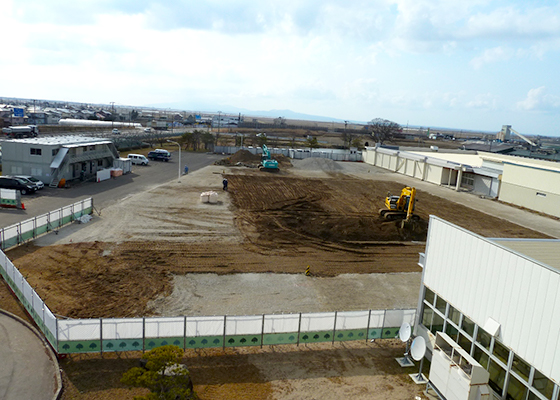

Ground concrete reused as gravel (white areas) (September–October 2018)
Effective Use of Rain and River Water (Thailand: Bang Pa-in Plant)

Bang Pa-in Plant's rainwater reservoir and rainwater reuse facility
In Thailand, our plants collect rainwater in a reservoir on the plant grounds and purify it at rainwater reuse facilities for reuse as industrial water, thereby reducing the amount of tap water used.
In addition to this system, one of the Thai plants took further steps in FY2012 to substantially reduce tap water consumption by drawing water from the nearby Chiang Rak Noi Canal and purifying it to use as an alternative to tap water. With the start of this system, the plant has reduced both its tap water consumption and its water related costs.
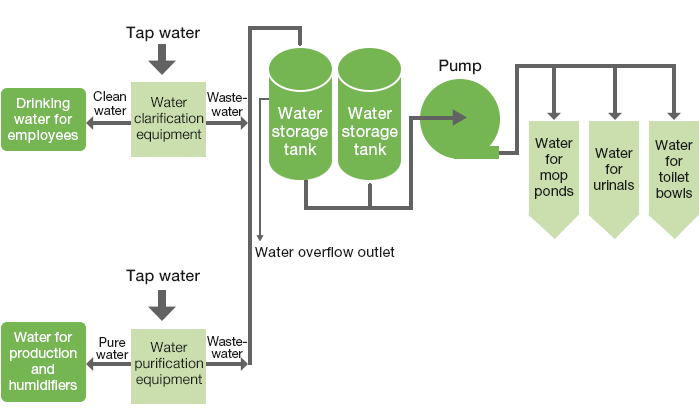
Recycling Water Resources and Reusing Wastewater (China: Qingdao Plant)
At Qingdao Plant, for the purpose of reusing water resources, a wastewater treatment equipment that allows wastewater discharged from water clarification equipment (use: to clarify drinking water for employees) and water purification equipment (use: water for production and humidifiers) to be stored in tanks and reused in toilets was newly installed.
Effect: Saves approx. 5,000 m3 of water per year, reducing approx. RMB 250,000 (415,000 yen) per year
Action to Reduce Waste Plastic (Cambodia)
Waste collection, separation, and disposal are becoming a major social issue in Cambodia, which has inadequacies in its social infrastructure and education system. The Cambodia plant started initiatives to reduce plastic waste at its cafeteria, one of the first to do so in Cambodia.
Approximately 9,000 local employees undertook bottom-up measures with high environmental awareness, changing the sale of fruits at its cafeteria from using disposable plastic bags to reusable plastic plates in March 2019. This reduced plastic bag use by approximately 160,000 bags—or a weight of 312 kg—per month. Going forward, the use of bamboo straws and reusable plastic cups is also being considered, with plans to further reduce plastic waste by 100,000 units per month.
Plastic waste was also raised as an important theme at the G20 Osaka Summit (held in June 2019), and it is becoming a global social issue. MinebeaMitsumi shares the success story at Cambodia with the entire Group, and the approximately 100,000 employees unite as one to undertake waste plastic reduction.

Future Issues and Goals
For FY2019, the Group's goal is to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfill by 12% per basic unit of production compared with FY2015.
In addition, we are presently conducting a survey of the current situation, and market analysis, of waste products disposed of as landfill with the aim of achieving still further reductions in the future.














