Initiatives for Effective Use of Resources Back Number (2014)
Back to Latest Initiatives for Effective Use of Resources
Basic Approach
The Minebea Group recognizes that there are limits to the availability of resources used in its products, which include metals, plastics, and other raw materials, along with oil, natural gas, and other energy sources. Additionally, with regard to rare earth elements indispensable to the manufacture of electronics, since the number of countries producing and exporting the materials is limited, they are more susceptible to export restrictions.
We believe that the effective use of resources is critical to the continuation of our business activities, and to that end we are taking various management measures.
Results of FY2013 Initiatives
 In FY2013, principal raw materials used by Minebea Group included approximately 87,800 tons of steel and 8,200 tons of resin, with the total amount of materials used increasing by approximately 23% compared to the previous fiscal year.
In FY2013, principal raw materials used by Minebea Group included approximately 87,800 tons of steel and 8,200 tons of resin, with the total amount of materials used increasing by approximately 23% compared to the previous fiscal year.
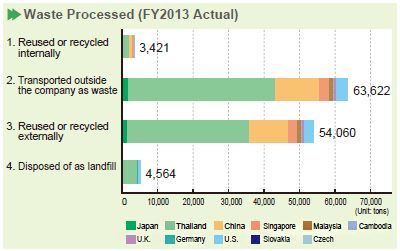
The amount of landfill waste generated by the Group's operations in FY2013 totaled 4,564 tons. As a result, the amount of landfill waste in FY2013 increased by 234 tons compared to FY2012.
At our mass production plants in Thailand and China, we are recycling water inside the plants to the greatest extent possible and prevent external emissions through our "Plant Wastewater Zero System." Water emissions from Group plants in FY2013 totaled 697,000 m3, a decline of 87,000 m3 compared with FY2012.

Initiatives at Business Sites
Participation in thermal recycling (Yonago and other plants)
Up until seven or eight years ago, only certain types of waste plastics from the Yonago Plant were recycled into reusable materials. Since then, the waste plastics have been collected as RPF* raw materials, and today nearly all the waste plastics are converted into RPF at a contractor's facilities and reused in an electric power boiler at a paper manufacturing company.
In FY2013, the Yonago Plant generated about 41 tons of waste plastic and was able to recycle 98.1% of the waste into RPF materials through the establishment of internal waste separation standards and progress in recycling activities. Waste plastics from the Karuizawa and Hamamatsu plants are also being converted into RPF raw materials.
* RPF (Refuse Paper & Plastic Fuel) :
A solid fuel made primarily from waste plastics and difficult-to-recycle paper. RPF generates a high amount of heat, on par with coal and oil, propelling its demand as an alternative to fossil fuels.

RPF made from waste plastic and difficult-to-recycle paper

Yonago Plant storage area for recyclable waste plastics
(black containers are for recyclable plastics)
Cumulative Profits from 3R Activities (China)
Minebea Shanghai launched its 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) Committee in 2003 to spearhead efforts to effectively use and reduce the amount of industrial waste. Though at the beginning we paid contractors to dispose of and process most of the industrial waste, collection and separation initiatives have made it possible to sell some of the waste for a profit. From the start of the effort in 2003 through the end of FY2013, the total earnings from the waste sales have reached 100 million RMB (about ¥1.8 billion).

Effective Use of Rain and River Water (Thailand)

Rainwater reservoir and rainwater reuse system at the Bang Pa-in Plant
The areas around the Bang Pa-in Plant, located near the capital of Bangkok, face a chronic shortage of tap water. The plant is striving to solve this community issue by lowering its tap water consumption through a rainwater reuse system which collects rainwater in a reservoir and purifies it for use within the plant.
In addition to this system, the plant took further steps in FY2012 to substantially reduce its tap water consumption by drawing water from the nearby Chiang Rak Noi Canal and purifying it to use as an alternative to tap water. With the start of this system, the plant has reduced both its tap water consumption and its water-related costs.
Conversion of Raw Kitchen Waste into Biogas (Thailand)

Biogas generation equipment
Minebea subsidiaries in Thailand are taking part in a project by the Thai Ministry of Energy to promote the recycling of raw food waste into biogas energy. Both the Bang Pa-in and the Lop Buri plants have installed biogas generation systems on site. The generated biogas, which boasts a low environmental footprint, is used as an alternative to LP gas for cooking meals in the cafeterias.
Recycling of Vials and Other Materials (domestic logistics warehouses)
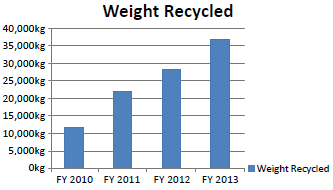
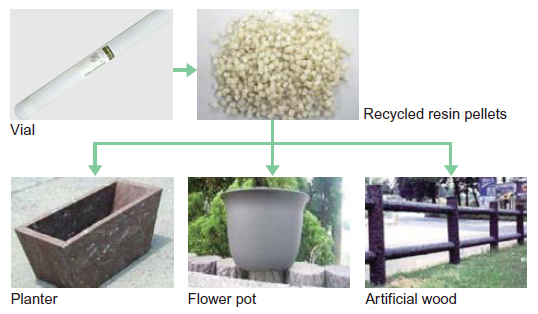
Since FY2010, the Minebea Group has sold as recyclable materials the polyethylene product containers (vials), stretch films, and polypropylene bands used in product deliveries to customers.
In FY2013, about 37 tons of vials, stretch films, and polypropylene bands were reprocessed into resin pellets and then recycled into planters and flower pots, as well as imitation trees.
Future Issues and Goals
For FY2014, we have set a target of limiting the amount of landfill waste to 4,850 tons following a recalculation of previous results. Currently, we are researching the types of landfill waste we generate and conducting market analysis in an effort to further lower waste amounts in the future.














